
Difference: ExperimentalqPCR (1 vs. 4)
Revision 42022-07-19 - KateElston
| ||||||||
| Deleted: | ||||||||
| < < | THIS PAGE IS CURRENTLY UNDER CONSTRUCTION | |||||||
<<Return to qPCR page
Experimental qPCR Plate Setup and AnalysisGoals
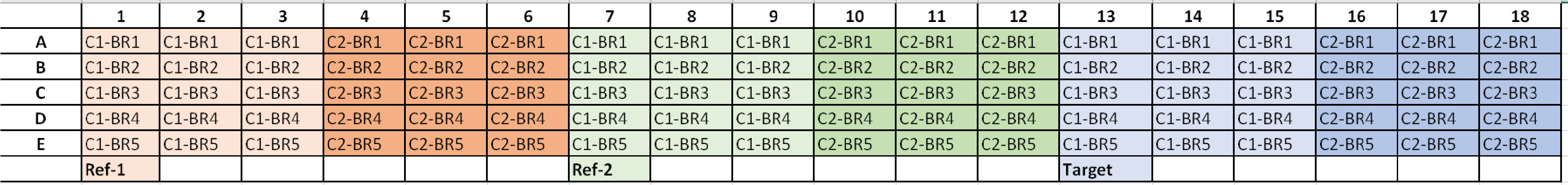 *C1 = Condition 1, C2 = Condition 2, and BR# = Biological Replicate
Conditions
*C1 = Condition 1, C2 = Condition 2, and BR# = Biological Replicate
Conditions
| ||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||
| > > | Note: Keep your diluted cDNA samples at 4°C to avoid complications with freeze/thaw | |||||||
What you are looking for
AnalysisI like to perform my qPCR analysis using the pfaffl method, a brief description of which is shown below:The Pfaffl method... is used to calculate relative gene expression data while accounting for differences in primer efficiencies. Unlike the delta-delta Ct method, which assumes primer efficiencies are similar between the gene of interest and the housekeeping gene, the Pfaffl method accounts for any efficiency differences to increase reproducibility. | ||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||
| < < | To perform the pfaffl method I've found that the best guide is this website | |||||||
| > > | To perform the pfaffl method I've found that the best guide is this website | |||||||
<<Return to qPCR page
| ||||||||
Revision 32020-04-09 - KateElston
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < < | <<Return to qPCR page | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > > | THIS PAGE IS CURRENTLY UNDER CONSTRUCTION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > > | <<Return to qPCR page | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Experimental qPCR Plate Setup and AnalysisGoals
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < < |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > > | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > > | Typical plate setup with 2 reference genes and a target gene:
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < < |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > > | *C1 = Condition 1, C2 = Condition 2, and BR# = Biological Replicate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Deleted: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < < |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Conditions
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < < |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
What you are looking for
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Changed: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < < | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > > | Analysis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > > | I like to perform my qPCR analysis using the pfaffl method, a brief description of which is shown below: The Pfaffl method... is used to calculate relative gene expression data while accounting for differences in primer efficiencies. Unlike the delta-delta Ct method, which assumes primer efficiencies are similar between the gene of interest and the housekeeping gene, the Pfaffl method accounts for any efficiency differences to increase reproducibility.To perform the pfaffl method I've found that the best guide is this website | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| <<Return to qPCR page | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Added: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > > |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revision 22020-04-09 - JuliePerreau
Experimental qPCR Plate Setup and AnalysisGoals
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Changed: | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| < < |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| > > |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
What you are looking for
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Revision 12019-03-21 - KateElston
Experimental qPCR Plate Setup and AnalysisGoals
|
Ideas, requests, problems regarding TWiki? Send feedback